Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea (gah-nuh-REE-uh) is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) spread through all forms of sexual intercourse. It also can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Gonorrhea can affect the genitals, urethra * , rectum * , eyes, throat, joints, and other organs and tissues of the body.
* urethra (yoo-REE-thra) is the tube through which urine passes from the bladder to the outside of the body.
* rectum is the final portion of the large intestine, connecting the colon to the anus.
KEYWORDS
for searching the Internet and other reference sources
Antibiotic resistance
Chlamydia
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Sexually transmitted diseases
Venereal diseases
What Is Gonorrhea?
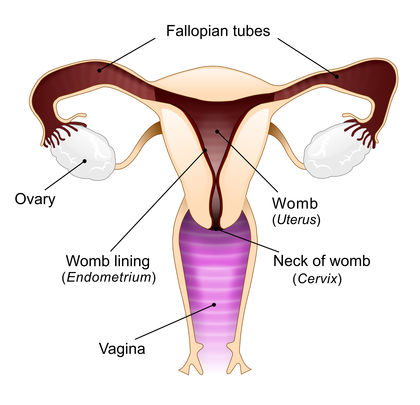
Gonorrhea is an infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae (nye-SEER-e-uh gah-no-REE-eye), which can grow in moist areas of the body including the vagina, penis, rectum, eyes, and throat. Gonorrhea may cause a discharge from the penis or vagina and pain while urinating. In women, the infection usually starts within the vagina at the cervix * ; if untreated, infection can spread to the uterus * and fallopian tubes * and result in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID); PID refers to an infection of a woman's reproductive organs, including the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and ovaries * , sometimes with spread of infection to other body tissues near these organs. Babies born to mothers who have gonorrhea can develop eye infection which, if untreated, can lead to blindness and other complications.
How Common Is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported STD in the United States, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); chlamydial infection * is number one. The CDC reports that the number of cases has been decreasing since the mid-1980s. However, up to 400,000 new cases are reported every year in the United States, and many more go unreported. Some experts estimate that as many as 2 million cases occur per year.
Gonorrhea is most common in highly populated urban areas and in people who have more than one sexual partner, but anyone who has sexual relations with an infected person can contract gonorrhea. Most men who contract the disease are ages 20 to 24; most women are under 21.
Is Gonorrhea Contagious?
Gonorrhea is contagious. When people do not use condoms or other protective measures when having sex or have multiple sexual partners, their risk of contracting the disease increases. From the time someone is infected with the gonorrhea bacterium, that person can spread the disease until properly treated.
The bacteria that cause gonorrhea are spread through body fluids, such as fluid from the vagina or semen * , that are passed from one person to another during vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse. Infected women can pass the infection to their babies during childbirth.
People can infect themselves if they touch an affected area and then rub or scratch their eyes. Gonorrhea can also be spread through kissing if one partner has a cut on the lip, but this way of becoming infected is rare. Sharing towels and sitting on toilet seats that have come in contact with the bacteria do not spread the disease.
* cervix (SIR-viks) is the lower, narrow end of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
* uterus (YOO-teh-rus) is the muscular, pear-shaped internal organ in a woman where a baby develops until birth.
* fallopian (fah-LO-pee-uhn) tubes are the two slender tubes that connect the ovaries and the uterus in females. They carry the ova, or eggs, from the ovaries to the uterus.
* ovaries (O-vuh-reez) are the sexual glands from which ova, or eggs, are released in women.
* chlamydial (kla-MIH-dee-ul) infection can occur in various forms in which the bacteria can invade the urinary and genital systems of the body, as well as the eyes and lungs. One of its most common forms is a sexually transmitted disease (STD), usually passed from one person to another through unprotected sexual intercourse.
* semen (SEE-men) is the sperm-containing whitish fluid produced by the male reproductive tract.
How Do People Know They Have Gonorrhea?
Many people who contract gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. For those who do, the symptoms often are mild. Males are much more likely to know they have gonorrhea than females, but up to 20 percent of males do not experience any symptoms at all. Within 2 weeks after being infected, males often feel burning when urinating and have pain or a greenish discharge from the penis. The lymph nodes * in the groin may swell, and the head of the penis may become irritated and red.

Although many women with gonorrhea have mild or no symptoms, those who do develop symptoms usually begin to experience them within 2 to 3 weeks after contact with the bacteria. These include bloody or greenish-yellow discharge from the vagina, pain during urination and/or sexual intercourse, and itching, soreness, or redness in the genital area. Other symptoms, including abdominal * pain, bleeding during or after intercourse, and bleeding between periods may mean a woman has PID.
How Do Doctors Diagnose and Treat Gonorrhea?
Because the symptoms of gonorrhea are similar to those of chlamydial infection, doctors usually test a person experiencing symptoms for both of these STDs.
Diagnosis
A sample of genital fluid or discharge from the tip of the penis, vagina, cervix, or rectum can be tested for Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria by doing a culture. Results are usually known within 48 hours. Another test, polymerase (pah-LIM-er-ace) chain reaction (PCR), can be used to look for DNA * from the bacteria in urine, fluid from the cervix, or from swabs taken from the urethra. This test gives faster, accurate results.
Pharyngeal (fair-un-JEE-ul), or throat, gonorrhea can be detected by doing a throat culture. In newborns at risk for the disease, doctors swab the baby's eye discharge and do a culture to confirm the diagnosis. Gonorrheal eye infection is uncommon in U.S. infants because newborns routinely receive antibiotic eye drops or ointment at birth to prevent infection.
Treatment
Gonorrhea is curable when treated with antibiotics, although some strains * of the bacteria are becoming resistant to medication. It is important to stop having sexual relations while infected, and all sexual partners should be told and tested, even if they do not have symptoms. If they have the disease they should also be treated with antibiotics. People who have both gonorrhea and chlamydial infection are treated with a combination of antibiotics. Infected newborns are given antibiotics intravenously (directly into a vein).
With antibiotic treatment, gonorrhea usually clears up within 2 weeks. It is important to take the full course of medication even if the symptoms get better, and to contact the doctor if they do not. When treated early, there are usually no long-term complications.
* lymph (LIMF) nodes are small, bean-shaped masses of tissue that contain immune system cells that fight harmful microorganisms. Lymph nodes may swell during infections.
* abdominal (ab-DAH-mih-nul) refers to the area of the body below the ribs and above the hips that contains the stomach, intestines, and other organs.
* DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid (dee-OX-see-ry-bo-nyoo-klay-ik AH-sid), is the specialized chemical substance that contains the genetic code necessary to build and maintain the structures and functions of living organisms.
* strains are various subtypes of organisms, such as viruses or bacteria.
* ectopic (ek-TAH-pik) pregnancy is an abnormal pregnancy in which the fertilized egg develops outside the uterus, usually within one of the fallopian tubes.
Complications
If a person has had gonorrhea before, it does not reduce the chances of becoming infected again. In fact, it increases the likelihood that complications may occur. In women, untreated gonorrhea can lead to PID, which can cause ectopic pregnancy * and sometimes lead to infertility (the inability to become pregnant). Ectopic pregnancies require emergency surgery; an ectopic pregnancy that bursts can cause massive bleeding and even death.
Without treatment, gonorrhea can spread throughout the body, through the blood, and to the joints, heart, and brain, although this rarely occurs in young people who are in good health. Newborns who are not treated for gonorrheal eye infection are at risk for blindness. People with untreated gonorrhea are more likely to contract HIV * if they have unprotected sex with someone who is HIV-positive.
Can Gonorrhea Be Prevented?
The best way to avoid contracting or spreading gonorrhea is to abstain from sexual intercourse. For those who do have sex, using a latex condom properly during all forms of intercourse is important. Doctors advise women who are sexually active to have a yearly gynecological exam with STD screening. They also recommend that people with any symptoms of gonorrhea or who are at risk for STDs see a doctor. If a person is found to have gonorrhea, all sexual partners also need to be tested and treated.
* HIV, or the human immunodeficiency (HYOO-mun ih-myoo-no-dih-FIH-shen-see) virus, is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
Resources
Organizations
U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID),
Building 31, Room 7A-50, 31 Center Drive MSC 2520, Bethesda, MD
20892-2520. The NIAID posts fact sheets about many STDs, including
gonorrhea, at its website.
Telephone 301-496-5717
http://www.niaid.nih.gov
Planned Parenthood Federation of America, 810 Seventh Avenue, New York,
NY 10019. Planned Parenthood posts information about sexually
transmitted infections at its website.
Telephone 212-541-7800
http://www.plannedparenthood.org
Website
KidsHealth.org
. KidsHealth is a website created by the medical experts of the Nemours
Foundation and is devoted to issues of children's health. It
contains articles on a variety of health topics, including gonorrhea and
other STDs.
http://www.KidsHealth.org
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: