Substance Abuse

Substance abuse is the misuse of alcohol, tobacco, illegal drugs, prescription drugs, and other substances (such as paint thinners or aerosol gasses) that change how the mind and body work. It is possible to abuse some substances without becoming physically, emotionally, or psychologically dependent on them, but continued use does tend to make people dependent. Dependency on some substances happens very quickly and is difficult to reverse.
KEYWORDS
for searching the Internet and other reference sources
Addiction
Drug abuse
Narcotics
Tobacco
What Is Substance Abuse?
Substance abuse is a serious problem in the United States. People who abuse substances can get sick, ruin their relationships with other people, destroy their lives and the lives of family members, and even die. Substance abuse contributes to accidents, crime, violence within the family, and lost productivity at work.
Substance abuse is the use of any substance for an unintended purpose or in an excessive amount. All substances, whether legal or illegal, have an impact on health when used in the wrong way. Different sub-stances have different effects on the body. Substances that are commonly abused in the United States include:
- alcohol
- amphetamines
- anabolic steroids
- cocaine
- depressants
- hallucinogens
- inhalants
- marijuana
- narcotics
- prescription medications
- nonprescription (over-the-counter) medications
- tobacco
Dependency and addiction
People can abuse some substances without being physically, emotionally, or psychologically dependent on them, although continued use often leads to dependency. With continued use, the tolerance for a substance tends to grow, so that to get the same effect a person must use more and more of the substance. Some substances are very quickly addictive.
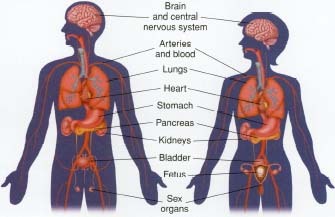
Addiction is a special type of dependence in which people have a compulsive need to use the substance no matter what the consequences are. People who are psychologically addicted want to keep using the sub-stance to feel satisfied. People who are physically addicted feel sick and have physical withdrawal symptoms if they stop using the substance. The risk and type of dependence varies by substance. Substance abuse occurs among people of all ages, from children to the elderly, including those with good educations and professional jobs.
Alcohol
Although moderate drinking (up to two drinks a day for men and one drink a day for women and older people) is not normally considered harmful, millions of people in the United States abuse alcohol or are alcoholics (people who are physically dependent on alcohol). A 1996 national survey found that 11 million Americans are heavy drinkers, and that 32 million people engage in binge drinking (more than five drinks on one occasion). This includes 1.9 million people with alcoholism and 4.4 million binge drinkers between the ages of 12 and 20.
Alcohol depresses the central nervous system. It interferes with messages to and from the brain, and alters the way that drinkers feel, see, hear, and move. People who drink too much may lose muscle coordina-tion, may become abusive to friends, may exhibit poor judgment, may drive while drunk and cause accidents, may anger easily and get into fights, may take foolish risks, may vomit violently, or may get arrested because of their behavior while under the influence of alcohol.
People with alcoholism are at risk for serious, even life-threatening diseases and problems. It increases the risk for certain cancers, and causes liver damage, immune system problems, and brain damage. Pregnant women who drink may permanently harm the development of their unborn children. Alcohol also increases the risk of death from car, on-the-job, and other accidents, and is a factor in many murders and suicides. Every year about 100,000 deaths are wholly or partially attributed to drinking alcohol. Alcoholism tends to run in families, and is a problem throughout the world.
Amphetamines
Amphetamines are man-made stimulants that speed up the central nervous system, creating a sense of euphoria, and increased energy. Ampheta-mines can be taken orally, injected, smoked, or sniffed. They may be legally prescribed to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), to suppress appetite, and to combat fatigue or narcolepsy (a disorder that causes uncontrolled falling asleep). Amphetamines include benzedrine, dexedrine, and methedrine. Street names for amphetamines include black beauties, crystal, hearts, ice, speed, and meth.
The U.S. and…
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) track statistics about health problems resulting from substance abuse. Notable facts:
- Almost 16,000 Americans died directly from use of legal or illegal drugs in 1997. This is more than two times the number of people who died from drug use in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This number, however, does not include deaths that might be indirectly related to drug use, such as homicides, accidents, or infant deaths resulting from the mother's drug use. It also does not include deaths related to other addictive substances like alcohol and tobacco.
- The death rate from drug use per 100,000 Americans also has increased, from 3 deaths per 100,000 people in 1980 to 6 deaths per 100,000 people in 1997. The rise of crack cocaine use and more potent heroin are among the reasons for the rise.
- Overall use of illegal drugs in the United States, however, fell by half between the mid-1980s and late 1990s. The peak year for use was in 1979, when 25 million people reported using illegal drugs at least once within the last month. By the late 1990s, the number had dropped to about 13 million people, or about 6 percent of people aged 12 and older.
- About 15 million people "incur a significant risk to their health" by abusing drugs, the World Health Organization said in 1996. Between 100,000 and 200,000 deaths per year are linked with injecting drugs, mostly from contracting AIDS and hepatitis from shared needles.
- Drug use is stabilizing in many industrial nations. But the use of drugs that are injected is rising in developing nations of Africa and Asia, leading to increases in hepatitis, HIV infections, and AIDS.
- Among the most commonly used drugs worldwide is marijuana. A 1997 estimate was that 141 million people, or 2 percent of the world's population, had used marijuana.
People who abuse amphetamines need more and more of the drug to achieve the same effect or high. When they become dependent, ampheta-mine users may be jittery, lose weight, feel depressed, anxious, restless, hostile, and lack energy. An overdose may cause a very fast heartbeat (tachycardia), high blood pressure, seizures, fever, delirium, paranoia * , psychosis * , coma, and cardiovascular collapse.
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids are synthetic compounds that are closely related to testosterone, the male sex hormone. Taken orally or injected, they may promote the growth of skeletal muscle and lean body mass, increase physical endurance, and cause serious side effects.
Steroids are used medically as hormone replacement therapy. Athletes, especially weight lifters and body builders, sometimes use steroids illegally to enhance their performance and to create extremely bulky muscles. A 1997 study by the National Institute on Drug Abuse estimated that up to 1.5 percent of all eighth, tenth, and twelfth graders in the United States had tried anabolic steroids. Men, however, are many times more likely to use steroids than women.
Some of the short-term side effects of steroids often are reversible, including aggressive behavior, jaundice (a liver problem causing yellow skin, tissues, and body fluid), fluid retention, high blood pressure, severe acne, and trembling. Other side effects include:
- In males: shrinking testicles, infertility, reduced sperm count, baldness, development of breasts.
- In females: growth of hair on the face and body, a deepened voice, changes in the menstrual cycle, enlargement of the genitalia.
- In teenagers: acceleration of puberty and shortening of adult height because the skeleton matures too fast.
The effects of long-term, high-dose use of steroids are not completely known. They may cause increases in cholesterol, heart disease, liver tumors, cancer, and cataracts.
Cocaine
Cocaine, a white powder extracted from the leaves of the South American coca plant, is a stimulant that creates a rush of euphoria, increased physical energy, and sleeplessness. Cocaine can be snorted or sniffed, injected, or smoked. Street names include coke, dust, blow, and crack. Crack is a less expensive form of cocaine that has been processed for smoking. Crack produces a very intense, but short-lived high. Crack is the most addictive form of cocaine.
* paranoia (pair-a-NOY-a) refers to behavior that is based on delusions of persecution or grandeur. People with persecution delusions falsely believe that other people are out to harm them. People with delusions of grandeur falsely believe that they have great importance or ability,
* psychosis (sy-KO-sis) is a serious mental illness that leads to thoughts and behaviors that are out of touch with reality.
Athletic Competitions
The International Olympic Committee and most other organizations sponsoring national and international athletic competitions have banned more than 20 different anabolic steroids. The ban is enforced through sometimes-controversial drug testing. In 1983, 19 athletes were disqualified from the Olympics for use of banned steroids.
Cocaine is a dangerous drug. It constricts the blood vessels, dilates pupils, and increases temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. It can make users restless, irritable, and anxious. First time users occasionally have died suddenly. People who use a lot of cocaine, or who have been using it for a long time, may become paranoid and violent, may damage the soft tissue in their noses to the point where part of the nose collapses, may lose their
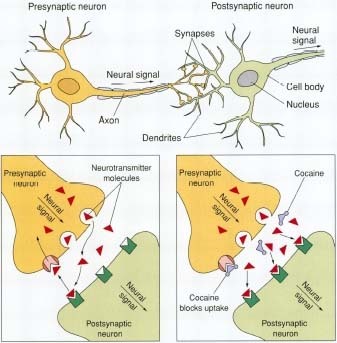
Cocaine, especially when smoked as crack, is very addictive. People who develop a tolerance to the drug need to use more to get the same high as the first time they used it, which may lead to participation in criminal activities. Withdrawal from cocaine addiction leaves the person feeling depressed, tired, sleepy, and sometimes suicidal, as well as having a strong craving for cocaine.
Depressants
Depressants slow down the nervous system, relieving anxiety, irritability, and tension. Depressants include barbiturates, methaqualone, and tranquilizers. They may be prescribed legally as a sedative, an anesthetic, to control anxiety, or to control seizures. Street names include barbs, roofies, and tranks. When depressants are combined with alcohol, the slowing effects on the nervous system are more powerful than when alcohol or depressants are used alone. Abuse of depressants causes users to become uninhibited, in a way similar to being drunk, which may be followed by sleepiness. An overdose may cause respiratory distress, coma, and death. Most depressants are physically and psychologically addictive.
Medicinal Marijuana
Marijuana is an illegal drug. In some states, however, legislation has been passed that allows doctors to prescribe marijuana for certain purposes. Research indicates that marijuana may help in the treatment of glaucoma, and may relieve the nausea and wasting away that people with AIDS and cancer sometimes experience as a side effect of other treatments. But research also shows that marijuana smoke contains moretarthan cigarette smoke and may contain high levels of other cancer-causing agents. Further research is needed and public policies regarding marijuana are likely to remain controversial.
* hallucinations are false perceptions. People hear voices, see visions, or otherwise sense things that are not really there.
* delusions are false beliefs that a person clings to, despite their lack of basis in reality.
The Opium Trade
Ancient Chinese medical texts indicated that opium, imported to the west from China by Arab traders in the eighth century, was used originally for medicinal purposes. When tobacco was introduced to China from the Philippines, the mixing of tobacco with opium became popular. British colonial traders recognized the strong demand for opium. Despite an eighteenth century edict by the Chinese government banning the sale of opium and the operation of opium houses, the British continued its sale on the black market. During the late eighteenth century, opium was at times the largest single commodity in trade.
Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens, also called psychedelic drugs, cause hallucinations * , delusions * , altered perceptions, and unpredictable behavior. LSD (lyser-gic acid diethylamide), usually called "acid," is one of the strongest hal-lucinogens. Taken orally, the effects of LSD are unpredictable, depending on the amount taken, the user's personality, mood, expectations, and the surroundings in which the drug is taken. LSD usually changes the user's sense of time and self, and can produce strange feelings ("hearing" colors or "seeing" sounds). Some users have scary thoughts and feelings about losing control, insanity, death, and despair. Physically, LSD causes dilated pupils; increases in body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure; loss of appetite; sweating; dry mouth; sleeplessness; and tremors. Users may experience flashbacks (recurrences) within a few days to more than a year after using LSD.
Other widely used hallucinogens are DMT (dimethyltryptamine), psilo-cybin (the main ingredient in "magic" mushrooms), MDMA ("ecstasy"), and mescaline. The effects of psilocybin and mescaline are similar to LSD. MDMA makes people feel less inhibited and distorts judgment.
Hallucinogens are not physically addictive, but people using them are at risk for accidents, violence, panic attacks, and other consequences of impaired judgment. All of these substances are illegal to use, make, or sell.
Inhalants
Inhalants are chemical vapors that can be breathed to produce mind-altering effects. Users inhale the vapors through their noses or mouths. The vapors then enter the lungs. There are three types of inhalants: sol-vents (such as paint thinners, gasoline, glues, felt-tip marker fluid), gases (such as butane lighters, whipping cream aerosols, spray paints, deodorant sprays, and nitrous oxide or "laughing gas"), and nitrites.
The physical effects of inhalants depend on the chemical being inhaled. Many cause serious, often irreversible health problems, and sometimes cause death. Users can lose consciousness. Other serious, but potentially reversible, effects include liver damage, kidney damage, and depletion of blood oxygen. Irreversible effects of inhalers include hearing loss, loss of muscle control and limb spasms, damage to the central nervous system and brain, damage to the bone marrow, lung damage, and heart failure.
Marijuana
Marijuana is a tobacco-like substance made from the hemp plant Cannabis sativa. Also called pot, weed, Mary Jane, and many other names, marijuana is usually smoked as a cigarette (called a joint or a nail). Some users mix marijuana into foods or brew it as tea.
Some marijuana users feel relaxed, experience mild euphoria, and become more sociable. Their perception is distorted, causing problems with memory, learning, thinking, and problem solving. Physically, mari-juana causes loss of coordination and makes the heart beat faster. Occasionally other drugs are mixed with or sprinkled on marijuana, causing hallucinations, paranoia, and delirium.
Long-term use of marijuana affects the brain, lungs, and heart. Learning and memory can be impaired, and people who smoke marijuana are at risk for the same health problems as people who smoke tobacco: coughing, chronic bronchitis, respiratory infections, and lung damage.
Marijuana is psychologically rather than physically addictive. Medical use of marijuana to treat glaucoma and increase the appetite in people with cancer and AIDS is controversial and continues to be studied.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a component of Chinese traditional medicine that has been practiced for at least 2,500 years. The treatment consists of inserting small needles into designated points in the body.
Acupuncture is sometimes used to reduce the physical symptoms of withdrawal from addictive substances and to relieve the depression, anxiety, and insomnia that often accompany treatment. Acupuncture is not a replacement for medical care, counseling, and self-help programs but may add to their effectiveness.
Narcotics
Narcotics are drugs that dull the senses. They are used medically to relieve pain. Narcotics can produce a sense of euphoria (a "high") followed by sleepiness, and a feeling of being in a fog. At least 20 opiates, a type of narcotic, are available in the United States. These include morphine, heroin, meperidine, and codeine. Many opiates have legitimate medical uses, but heroin, the most commonly abused opiate, does not.
Heroin is made from the seed of the Asian poppy plant. It is usually a brown or white powder that users inject, smoke, or sniff. Long-term use of heroin can lead to miscarriages, collapsed veins, infections of the heart lining and valves, abscesses, liver disease, pneumonia, and fatal overdoses. Infectious diseases such as AIDS and hepatitis can be spread from person to person by sharing needles used to inject heroin. Withdrawal from heroin causes pain, nausea, sweating, and a great deal of physical and mental discomfort. Withdrawal symptoms are most commonly treated with maintenance doses of methadone, but withdrawal from methadone must later be accomplished.
Tobacco
Nicotine, the active ingredient in tobacco, is one of the most widely used addictive drugs in the United States. Nicotine both stimulates and sedates the central nervous system. Tobacco is usually smoked, but it can also be snuffed (placed between the lip and gum or under the tongue), or chewed. Smoking cigars and pipes also is harmful.
Tobacco contains thousands of chemicals, including carbon monoxide and tar. Many of these play a role in disease. The more people smoke, the greater their risk of disease. Smoking accounts for about 30 percent of all cancer deaths, 20 percent of heart disease deaths, and more than 80 percent of chronic obstructive lung disease cases. People who smoke tend to get more colds and respiratory tract infections than other people. Pregnant women who smoke have a greater risk of having a miscarriage or stillborn child. Babies of smokers usually weigh less, have more respiratory infections, are at higher risk of ear infections and asthma, and have less effective lungs than other babies. Being around people who smoke (called passive smoking) also is harmful. Passive smoking increases the risk that nonsmokers will have the same health problems as smokers.
Smokers feel physical symptoms of withdrawal when they stop smoking. A patch that delivers nicotine through the skin, when combined with counseling, behavior modification, and self-help groups, often can be effective in helping people quit smoking.
Prescription and Over-the-Counter Drugs
People can abuse legal medicines by taking more than prescribed, using them for nonmedical reasons, or using them to treat unrelated illnesses. The most commonly abused prescription and over-the-counter medicines are stimulants, pain relievers, depressants (such as sleeping pills), cough and cold medicines, and laxatives.
Abusing these substances can cause physical and psychological dependence. Some prescription medications contain alcohol and narcotics—such as codeine—that are physically addicting. Combining alcohol with prescription and over-the-counter drugs, or mixing drugs, can change the effectiveness of the drugs and cause harmful side effects.
How Is Substance Abuse Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis
Substance abuse often is difficult to diagnose and treat. Doctors can screen for substance abuse through a medical history, a physical exam, and sometimes blood or urine testing, but doctors and family members often have a hard time convincing substance abusers that they need help. In many cases, substance abusers are more afraid of losing the drug and of withdrawal symptoms than of the health and safety consequences of continued use.
Treatment
Treatment for substance abuse consists of helping people stop using the substance, treating withdrawal symptoms, and preventing people from returning to substance abuse afterwards. Outpatient psychotherapy * and self-help groups can be effective. People with severe problems may require residential treatment programs. Treatment often is provided by doctors and organizations that specialize in substance abuse programs. Successful programs:
- Evaluate people for psychiatric or medical disorders.
- Teach them about the effects of the drug and their addiction.
- Offer mutual support and self-help groups.
- Provide individual and group psychotherapy.
- Offer a replacement for the substance being given up.
- Emphasize behavior changes that promote not using the substance.
- Offer rehabilitation and life skills training.
Even people who are successfully treated must guard against starting to use the abused substance again. People with serious medical or psychiatric symptoms, people who overdose on drugs, and people who have toxic reactions to drugs require immediate medical treatment.
* psychotherapy is treatment of mental disorders and behavioral problems through support, suggestion, persuasion, reeducation, reassurance, and insight.
Resources
U.S. National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), National Institutes of
Health, 6000 Executive Boulevard, Bethesda, MD 20892-7003. NIDA's
website posts fact sheets about anabolic steroids, heroin, inhalant
abuse, marijuana, methamphetamine, and many other topics. It also
provides hyperlinks to more than 50 other organizations that provide
information about substance abuse and its treatment.
http://www.nida.nih.gov
U.S. National Clearinghouse for Alcohol and Drug Information. This
service of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
(SAMHSA) focuses on prevention. Its website has a
Kids Area
in English and Spanish.
Telephone 800-487-4890
http://www.health.org/kidsarea.htm
U.S. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA),
National Institutes of Health, 6000 Executive Boulevard, Bethesda, MD
20892-7003. NIAAA's website posts fact sheets in English and in
Spanish about alcoholism, alcoholism and pregnancy, and treatment.
http://www.niaaa.nih.gov
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) World Services, 475 Riverside Drive, 11th
floor, New York, NY 10115. This self-help organization provides
referrals to local support groups and has information about the AA
program.
Telephone 212-870-3400
http://www.alcoholics-anonymous.org
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: