Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a condition that occurs when the body is exposed to high levels of the hormone cortisol. Symptoms may include muscle weakness, extra body fat, excess hair, and emotional problems.
KEYWORDS
for searching the Internet and other reference sources
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Cortisol
Endocrine system
Hormones
What Is Cushing's Syndrome?
Cushing's syndrome is an endocrine, or hormone * , condition. It occurs when the body is exposed to high levels of the hormone cortisol for long periods of time.
Cortisol and the endocrine system
Cortisol is a hormone essential for life. It is involved in maintaining blood pressure and the immune system and in the body's handling of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It also helps the body respond to stress. However, too much cortisol has negative effects on the body.
Usually, cortisol production is tightly regulated by the interactions of three parts of the endocrine system:
- A part of the brain called the hypothalamus (hy-po-THAL-mus) secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
- CRH signals gland attached to the brain, the pituitary gland, to release adrenocorticotropin (ACTH).
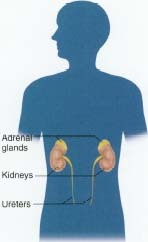
- ACTH signals the adrenal glands to make cortisol and release it into the bloodstream. The adrenal glands are a pair of organs located just above the kidneys in the abdominal cavity.
If something goes wrong with any of these glands or with the signaling system, the body may produce too much cortisol.
Tumors
Certain tumors, either cancerous or noncancerous, can cause Cushing's syndrome. For example, noncancerous pituitary tumors that secrete ACTH are a cause of the condition. Tumors elsewhere in the body, such as in the lungs, also can produce ACTH, and tumors of the adrenal glands can cause overproduction of cortisol. Most cases of Cushing's syndrome are not inherited, but the tendency to develop tumors can be inherited.
Cortisone-based therapies
Treatment with high doses of cortisone-based hormone medications for asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other inflammatory diseases is the most common reason people develop Cushing's syndrome.
* hormones are chemicals that are produced by different glands in the body. Hormones are like the body's ambassadors: they are created in one place but are sent through the body to have specific regulatory effects in different places.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of
Cushing's Syndrome?
In 1932, the American neurosurgeon Harvey Williams Cushing (1869—1939) described eight patients with symptoms of what later was named Cushing's syndrome. Dr. Cushing described how too much cortisol led to:
- obesity, especially of the face, neck, and upper body
- purplish stretch marks associated with weight gain
- thin and fragile skin that bruises easily
- slow wound healing
- weakened bones (osteoporosis)
- fatigue and weak muscles
- problems with sugar metabolism, which may lead to diabetes
- menstrual irregularities
- growth of excess hair
- high blood pressure
- irritability and depression.
How Is Cushing's Syndrome Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis
A doctor who sees a patient with symptoms suggestive of Cushing's syndrome will ask questions about the person's medical history and perform a physical exam. Laboratory tests, such as analysis of blood and urine, are used to measure cortisol levels. If cortisol levels are high, other tests are done to find out why. For example, imaging techniques for looking inside the body (such as CT scans * and MRIs * ) can be used to look for tumors.
Treatment
Treatment of tumors varies depending on the type. A tumor may be removed surgically, or it may be treated with radiation or chemotherapy. Sometimes Cushing's syndrome is treated with drugs to inhibit cortisol production. If Cushing's syndrome occurs as a side effect of hormone therapy, doctors can alter the dosage to minimize the side effects of the medication.
Altering hormone dosage and removal of tumors can lead to a full recovery, although sometimes the tumors come back. Because Cushing's syndrome can be difficult to diagnose, affected people sometimes live with the condition for years before it is diagnosed and treated.
* CT scans or CAT scans are the shortened names for computerized axial tomography, which uses computers to view cross sections inside the body.
* MRI means magnetic resonance imaging, which uses magnets to view inside the body.
Resources
The U.S. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney
Diseases (NIDDK) posts a fact sheet about Cushing's syndrome at
its website.
http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health/endo/pubs/cushings/cushings.htm
Cushing's Support and Research Foundation, Inc., 65 East India
Row 22B, Boston, MA 02110.
Telephone 617-723-3824
http://world.std.com/~csrf/
Pituitary Tumor Network Association, 16350 Ventura Boulevard, Number
231, Encino, CA 91436.
Telephone 805-499-9973
http://www.pituitary.com
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: