Yeast Infection, Vaginal
The vaginal yeast infection candidiasis (kan-di-DY-a-sis) is caused by an overabundance of a certain kind of fungus * in the genital area. Its symptoms include an itching or burning sensation in the genital area and, very typically, a white discharge from the vagina. Almost all cases of candidiasis affect women, although men also can show related signs of the infection.
KEYWORDS
for searching the Internet and other reference sources
Candida albicans
Candidiasis
Fungal infections
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
* fungus (FUN-gus) is any organism belonging to the kingdom Fungi (FUN-ji), which includes mushrooms, yeasts, and molds.
* yeast is a general term describing single-celled fungi that reproduce by budding.
What Is Candidiasis?
The fungus that causes vaginal yeast * infection is usually Candida albicans (KAN-di-da AL-bi-kanz). It is naturally present in many parts of
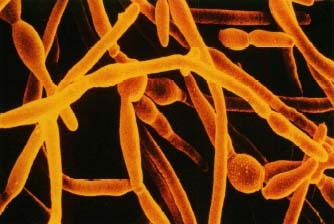
Candida fungus cells can multiply too much when the use of antibiotics * destroy too many of the bacteria that usually keep them in check. Other situations that may cause the fungus to grow out of control are the use of birth control pills, pregnancy, and the use of drugs that suppress the immune system * . When a woman has a disease like AIDS or diabetes that can cause weakening of the immune system, she will also be more likely to develop a vaginal yeast infection.
It is estimated that 75 percent of women have a yeast infection at least once in their life. Half of them will have the infection more than once.
What Are the Symptoms of Candidiasis?
The most notable symptom of vaginal yeast infection is a white discharge from the vagina. The discharge has the appearance of cottage cheese. The area around the vagina also may itch or feel irritated. In yeast infections in men, the head of the penis becomes inflamed or shows a rash.
How Is Candidiasis Diagnosed and Treated?
Vaginal yeast infection is easily diagnosed by examining a sample of the white vaginal discharge. Treatment is with antifungal drugs * that are applied to the affected area or taken by mouth in the form of a pill.
* gastrointestinal (GAS-tro-in-TES-ti-nal) means having to do with the stomach and intestines.
* bacteria (bak-TEER-ee-a) are single-celled microorganisms, which typically reproduce by cell division. Some, but not all, types of bacteria can cause disease in humans. Many types can live in the body without causing harm.
* antibiotics (AN-ty-by-OT-iks) are drugs that kill bacteria.
* immune system is the body system that fights disease.
* antifungal drugs (an-ty-FUNG-al drugs) are medications that kill fungi.
While some creams for vaginal yeast infections are available without a prescription, it is advisable to see a doctor the first time a vaginal yeast infection is noticed. It is important to have any infection diagnosed properly before treatment is started. Health professionals recommend that anyone with a vaginal yeast infection should also have her partner examined for infection.
How Can Candidiasis Be Prevented?
These steps can help prevent a vaginal yeast infection:
- Wearing cotton underwear
- Avoiding tight-fitting underwear made of synthetic fiber, like nylon
- Avoiding the daily use of panty hose
- Using white, nonperfumed toilet paper
- Keeping the genital area clean
- Using a towel (not a blow dryer) to dry the genital area
- Removing a wet bathing suit as soon as possible after swimming
- Avoiding douches and feminine hygiene sprays
- Using sanitary pads or tampons that are free of perfume
Antibiotics and Yogurt
Antibiotics prescribed to treat bacterial infections also kill beneficial bacteria. When the beneficial bacteria found normally in the vagina and other mucous membranes are killed, yeast cells can grow unchecked.
Eating active-culture yogurt daily while taking an antibiotic may help replenish the supply of beneficial bacteria.
Resource
Organization
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 1600 Clifton
Road N.E., Atlanta, GA 30333. The U.S. government authority for
information about infectious and other diseases, the CDC posts
information about vaginal yeast infections at its website and sponsors a
National Sexually Transmitted Diseases Hotline.
Telephone 800-227-8922
http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/candidiasis-gen-g.htm
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: